I , kirk evan maillet would like 2 WELCOME u 2 a magazine RENDERed BY myself WITHout paper since 1996

Church Silverhammer | Create Your Badge

310.594.8806 contact@lumal.com . .
|
|

|
|

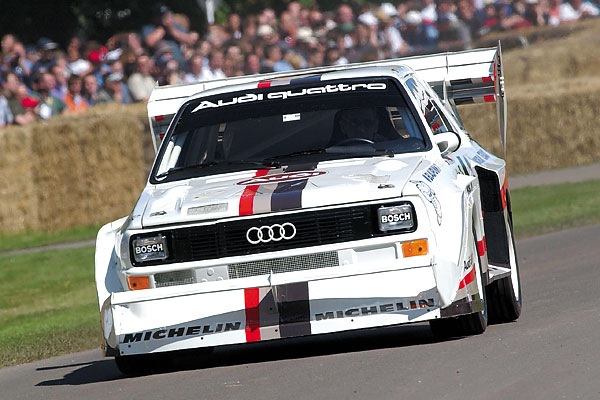
"vorsprung durch technik"

MORE part 2
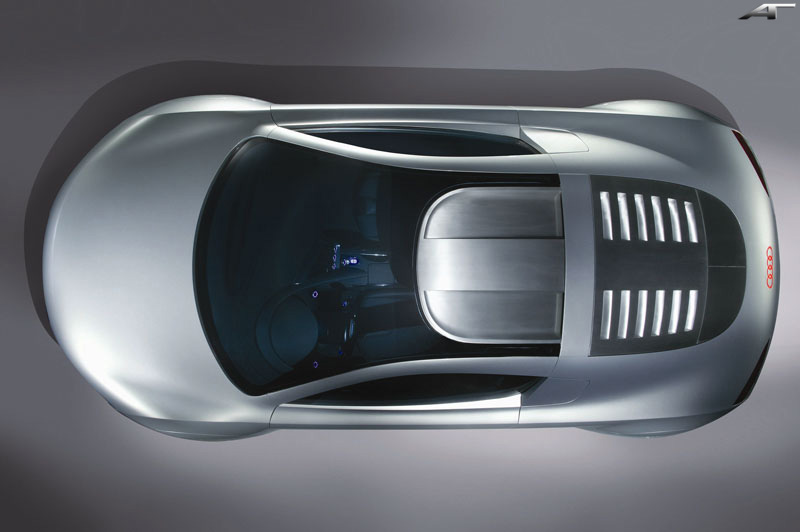








|
Acura //// Audi //// Austin-Healey //// BMW //// Buick //// Cadillac //// Chevrolet //// Chrysler Daihatsu //// Dodge //// Eagle //// Ford //// General Motors Corporation //// Geo //// Honda //// Hyundai //// Infiniti Isuzu //// Jaguar //// Jeep //// Jensen-Healey //// Kia //// Lexus //// Lincoln //// Mazda //// Mercedes Benz //// Mercury //// MG //// Mini Mitsubishi //// Nissan //// Oldsmobile //// Plymouth //// Pontiac //// Rolls-Royce //// Rover //// Saab //// Saturn //// Subaru //// Suzuki //// Toyota //// Triumph //// Volvo //// VW |

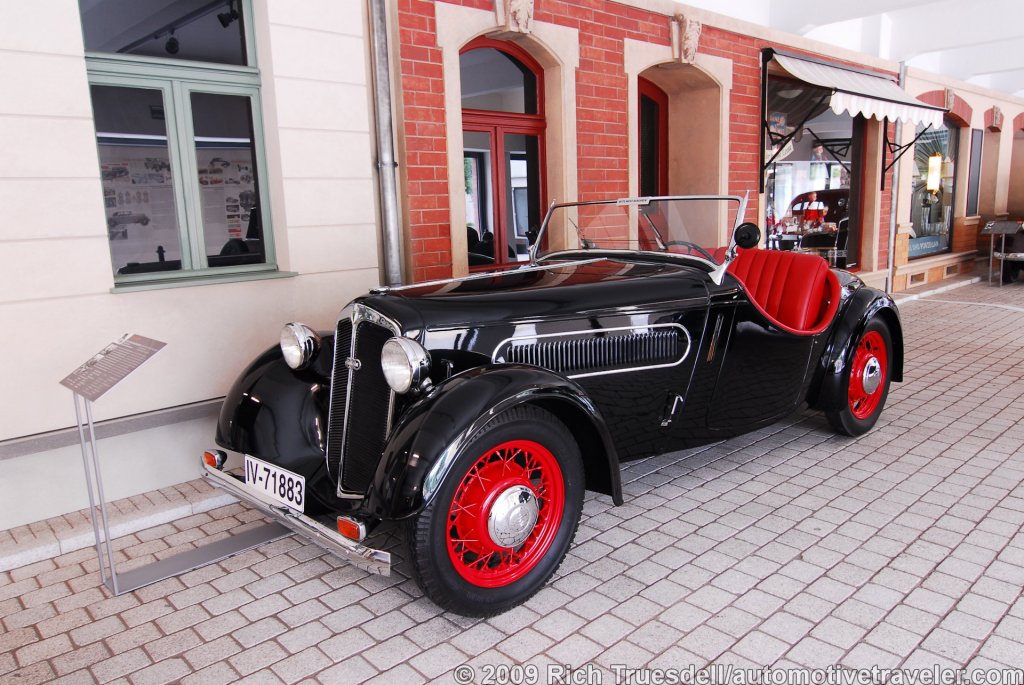
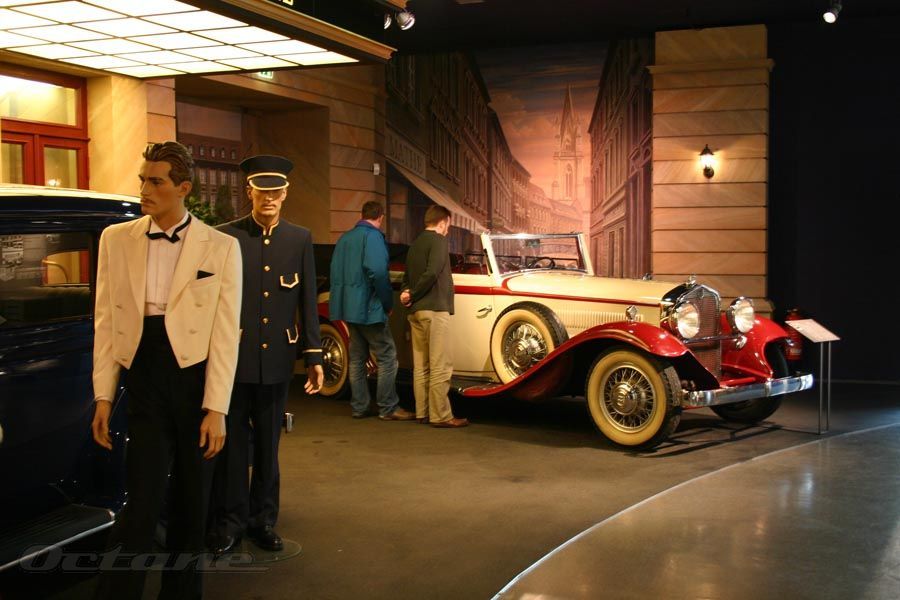
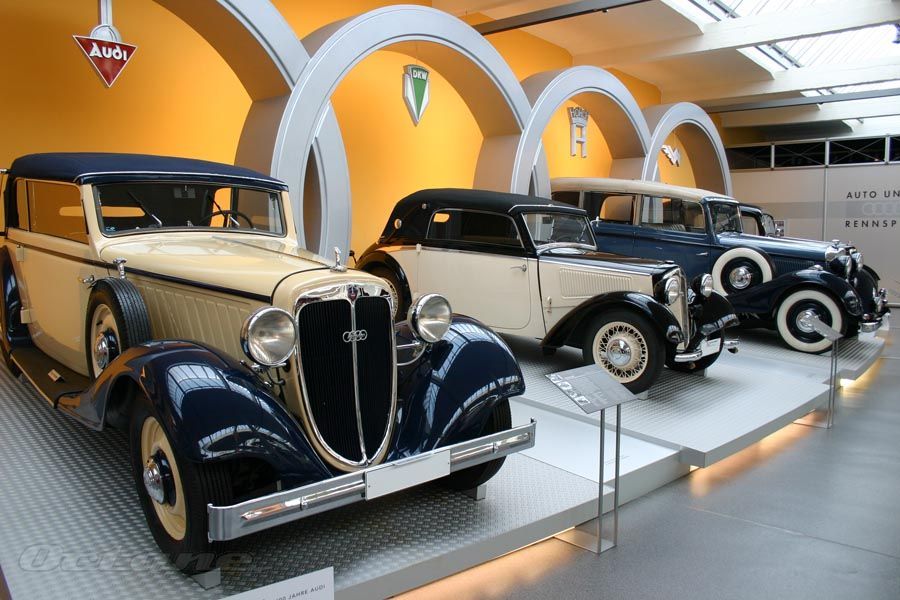
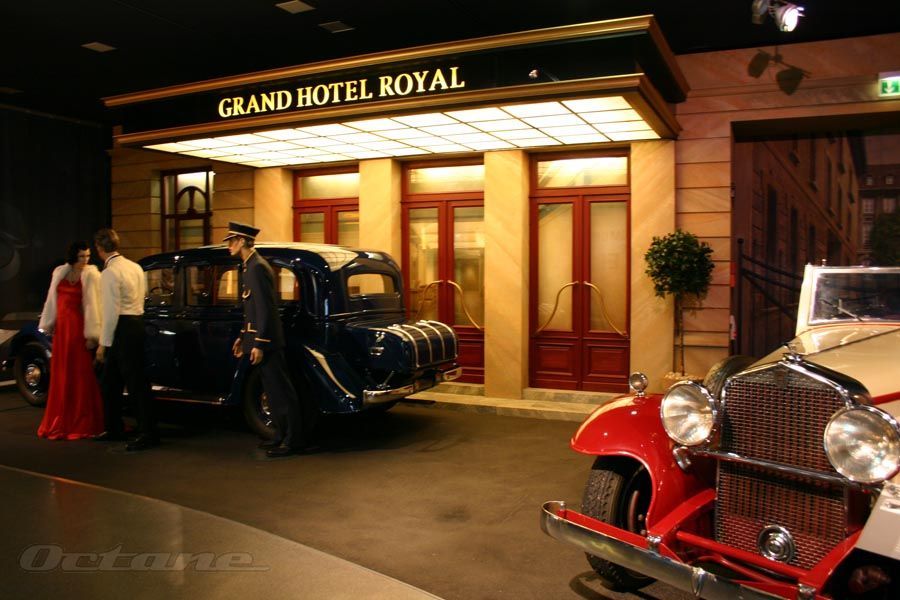
Audi The Audi badge the 'Four Rings' is the emblem of one of the oldest car manufacturers in Germany. It symbolises the 1932 merger of the four independent motor-vehicle manufacturers: Audi, DKW, Horch and Wanderer. Together with the NSU brand, which joined in 1969, these companies are the roots of the present-day AUDI AG. Join us on a journey through the development of the car and the birth of Audi.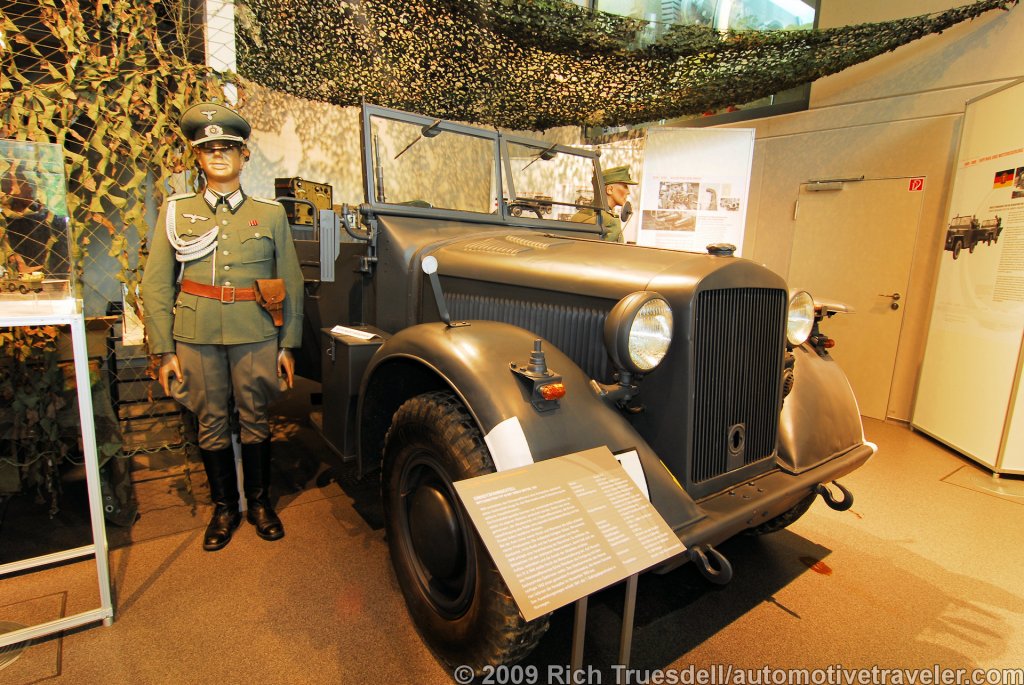 

In the late 1800's the automobile was invented. The technical
foundations of motorised transport had been decided: the thing
would have four wheels, one in each corner, and would be propelled
by an internal combustion engine. That much was certain, but not
much else. At this time, there were many heros of the automobile:
Gottfried Daimler and Carl Benz of Germany, Siegfried Marcus of
Austria, and the Americans, George Baldwin Seldon and Henry Ford. August
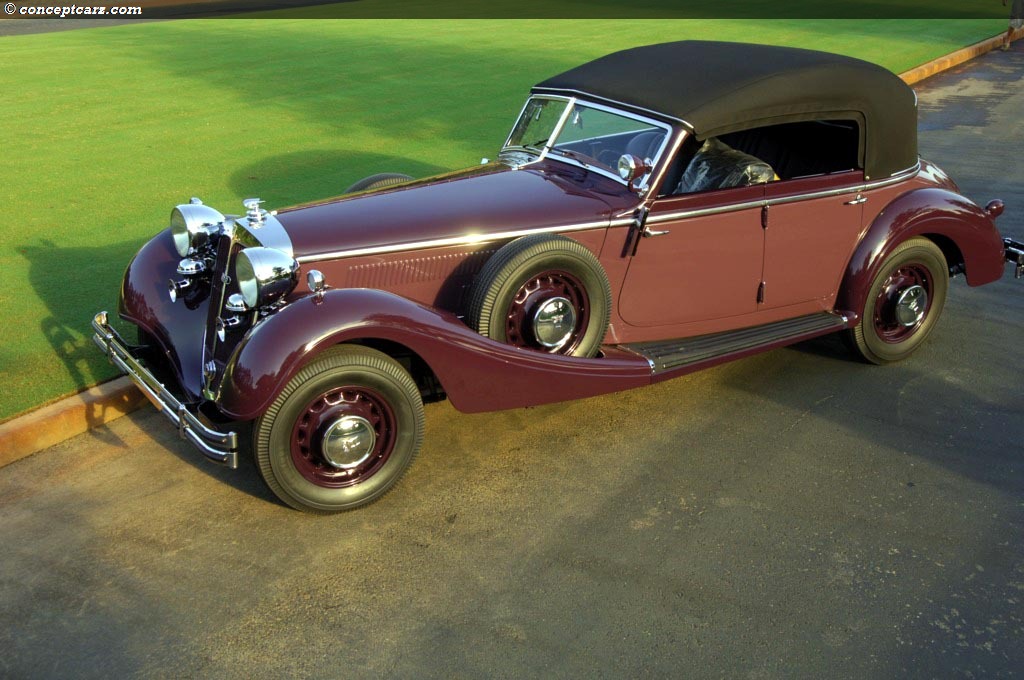
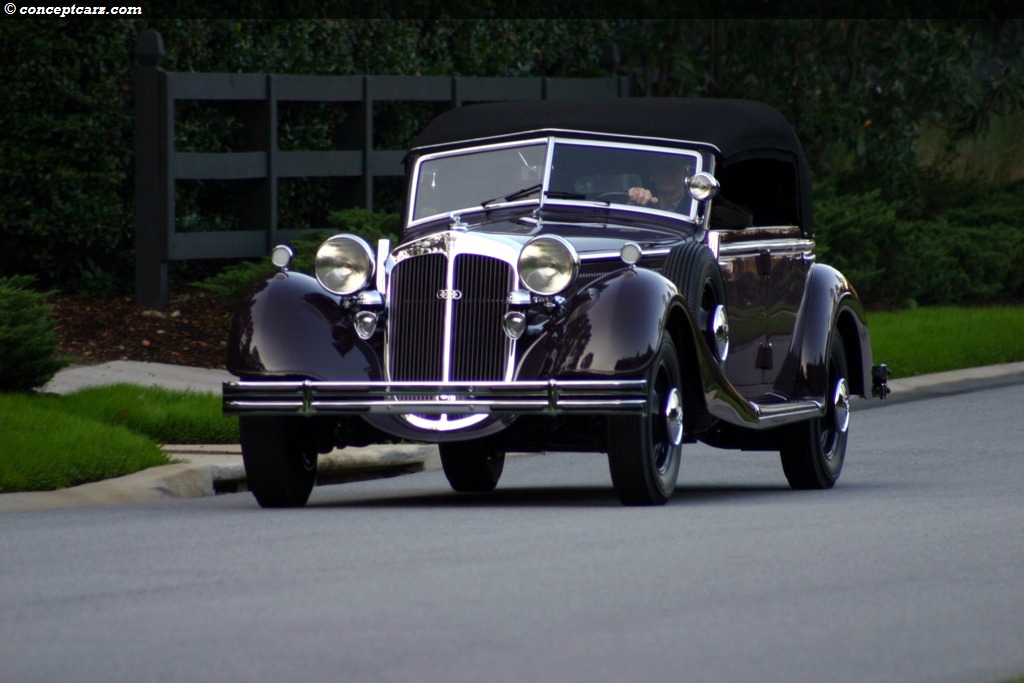
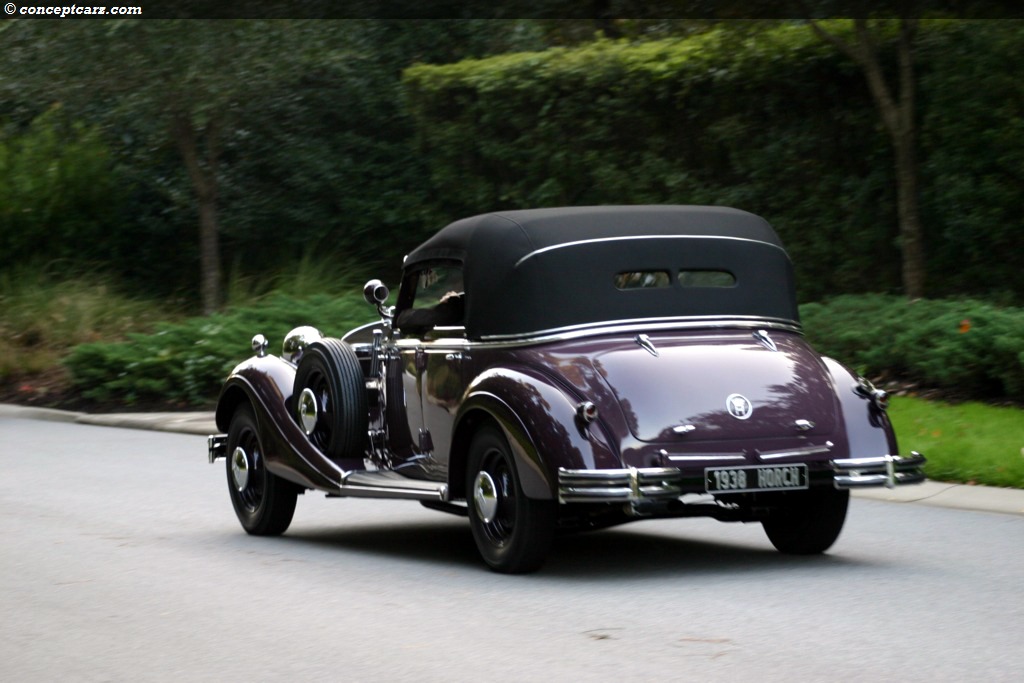
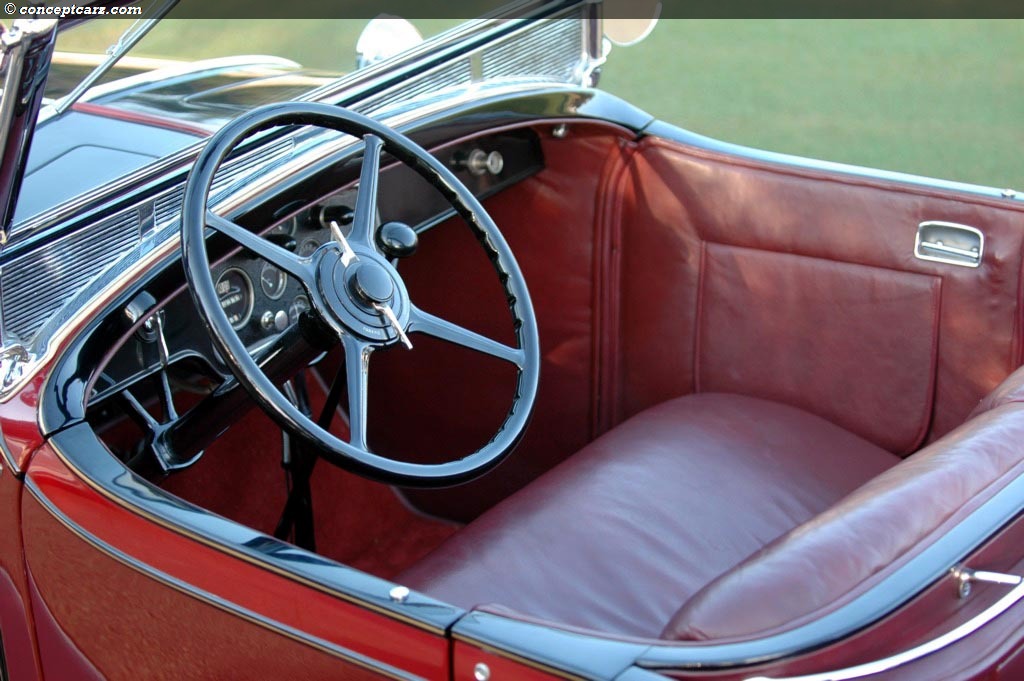
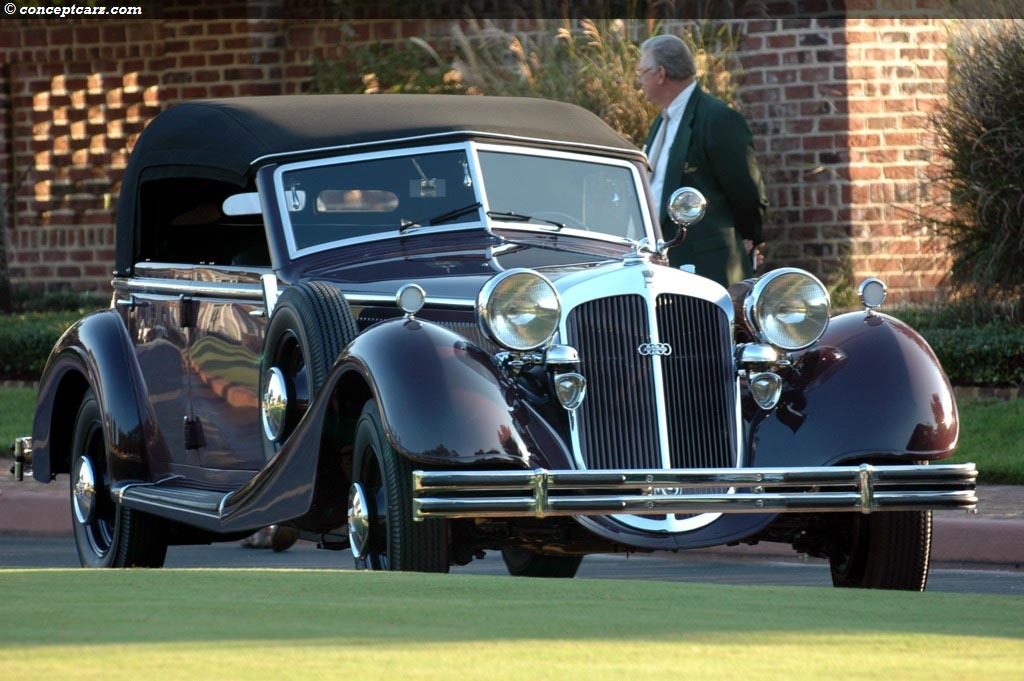
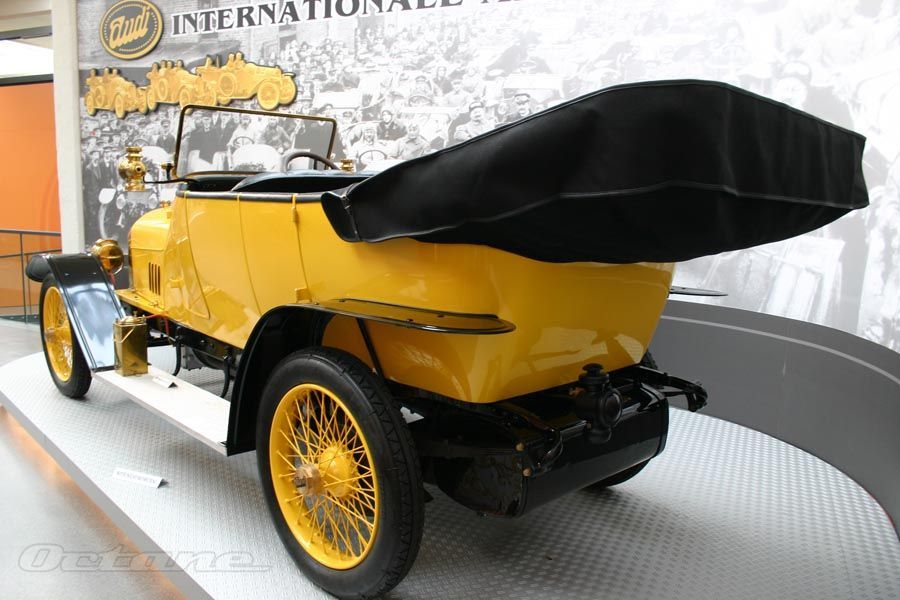
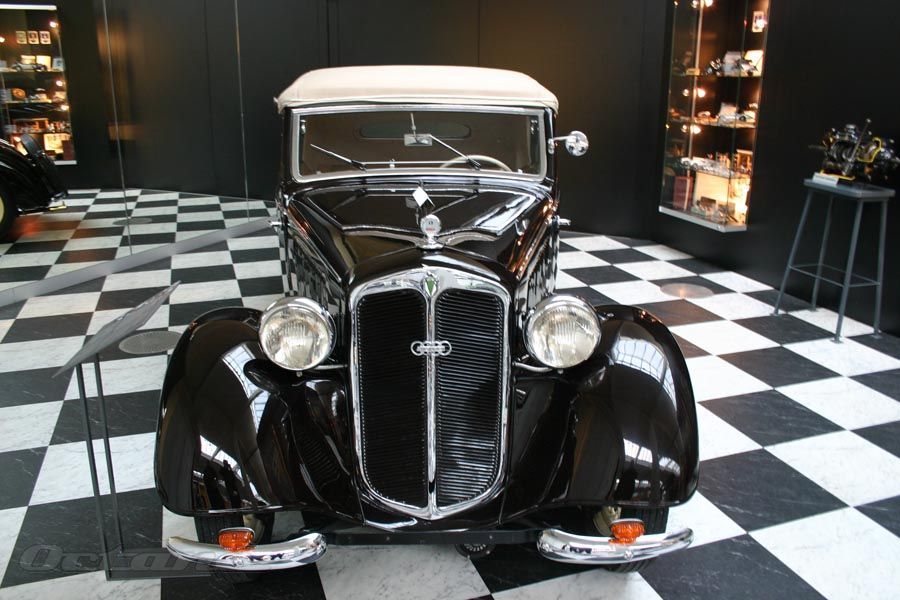
Horch built the elegant 'Audi Type K' for the discriminating tastes
of the elite. Many of these 1919 innovations would become
standard later on - for example left-hand steering and the central
position of the gear-shift. 3 built 2 destroyed after WWI 








From
the start, Auto Union AG was Germany's second largest automobile
manufacturer. 
Just when private cars were finally replacing bicycles in Germany,
the outcomes of the second world war had the most serious impact on
Auto Union. The plants were dismantled, and Auto Union was dissolved
by the Soviet military. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
- In December 1964, Auto Union was transferred to the Volkswagen
Group. The day of the two-stroke engine was over, and Auto Union engineers
had begun working full-time to develop a competitive four-stroke model.
Meanwhile, the VW 'Beetle' helped maintain production levels - From
1965 to 1969, between three and five hundred VW's were produced each
day at Ingolstadt. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - In 1967 Motor Distributors obtained the Audi franchise for the Republic of Ireland - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -1968
saw the unveiling of the first Audi 100 - a fundamentally new car which
helped renew the value of Auto Union.
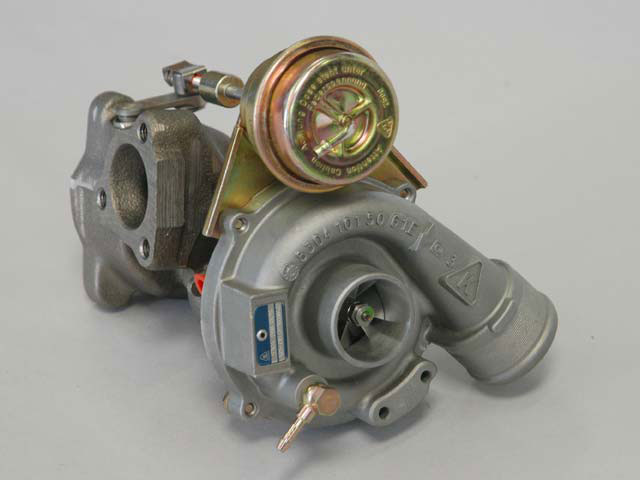
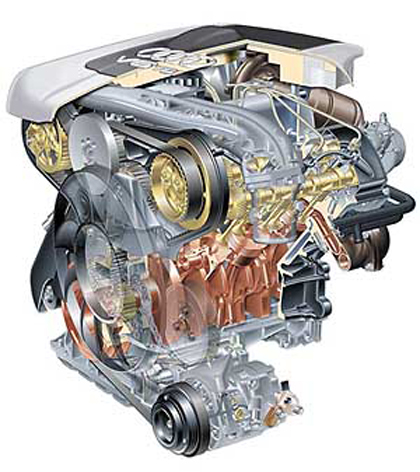



















December
1980 marks the landmark introduction of the first high
performance car built on four-wheel drive principles - the Audi
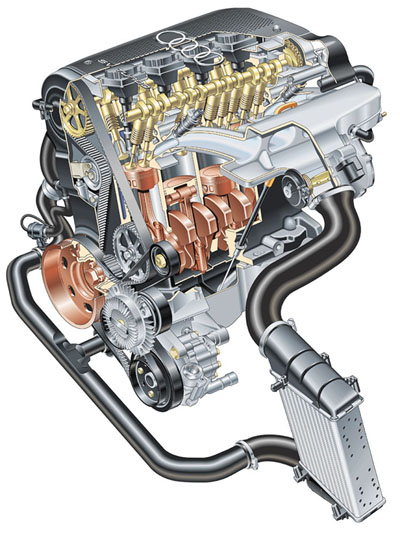
Quattro Coupe. Quattro is an Audi patented system that spreads
the car's power across all wheels, so the driver experiences improved
handling, greater stability, lower tyre wear, better traction
and therefore better safety in all road conditions.
Audi
NSU Auto Union AG was renamed Audi AG in 1985.
1990, the start of the last decade of the millennium, was
cause for celebration at Audi: the seven millionth Audi was produced
in Ingolstadt, and the Audi quattro was ten years old. But - as
always - Audi looked ahead, not behind, and the Board pledged to
become ‘the most attractive European marque’. The new improved Audi A8 and A4 give yet more evidence of Audi's
leadership in shaping the automotive world of tomorrow. The Audi
A3, launched in Ireland has set a new standard for luxury in the
compact class. And the Audi TT is the most recent evidence of
Audi's commitment to "Vursprung durch Technik".
Acura //// Audi //// Austin-Healey //// BMW //// Buick //// Cadillac //// Chevrolet //// Chrysler Daihatsu //// Dodge //// Eagle //// Ford //// General Motors Corporation //// Geo //// Honda //// Hyundai //// Infiniti Isuzu //// Jaguar //// Jeep //// Jensen-Healey //// Kia //// Lexus //// Lincoln //// Mazda //// Mercedes Benz //// Mercury //// MG //// Mini Mitsubishi //// Nissan //// Oldsmobile //// Plymouth //// Pontiac //// Rolls-Royce //// Rover //// Saab //// Saturn //// Subaru //// Suzuki //// Toyota //// Triumph //// Volvo //// VW  August Horch (12 October 1868 – 3 February 1951) was a German engineer and automobile pioneer, the founder of the manufacturing giant which would eventually become Audi. Beginnings: Horch was born in Winningen, Moselle and was educated in Mittweida. August Horch worked for Karl Benz from 1896, before founding A. Horch & Cie in November 1899, in Ehrenfeld, Cologne, Germany. Manufacturing The first Horch automobile was built in 1901. The company moved to Reichenbach in 1902 and Zwickau in 1904. Horch left the company in 1909 after a dispute, and set up in competition in Zwickau. His new firm was initially called Horch Automobil-Werke GmbH, but following a legal dispute over the Horch name, he was obliged to change the company name. (The court decided that Horch was a registered trademark on behalf of August Horch's former partners and August Horch was not entitled to use it any more). Consequently, Horch renamed his company Audi Automobilwerke GmbH in 1910, Audi being the Latinization of Horch. The Four Rings: In August 1928, the Danish engineer Jørgen Skafte Rasmussen of DKW acquired a majority holding in Audiwerke. In June 1932 Audi, DKW, Horch and Wanderer merged to form Auto Union AG, the new company's logo was four interlinked rings, one for each of the founder companies. Horch was on the supervisory board of Auto Union. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/August_Horch August Horch worked for Karl Benz for several years, rising to become factory manager at early automaker Benz & Company. In 1899 he established his own business, August Horch & Company, which had success for several years as a niche maker of technically advanced cars, including Germany's first vehicle with a four-cycle engine. In 1904 he took his business public, a move he later regretted, as stockholders voted him out of the company's presidency when sales slumped. In 1910 he founded a new company, Horch Automobile Works, which led to an immediate lawsuit alleging trademark infringement filed by Horch's first company. A court subsequently ruled that Horch & Company owned the rights to August Horch's name, so he renamed his second company Audi, a Latin translation of Horch, which literally means "hark". He retired in 1920, and died 30 years later. In 1932 Audi was merged with three other automakers (including Horch & Co.) to form Auto Union of Saxonian Motor Vehicle Builders, the corporate forebear of Audi AG, which is now a subsidiary of Volkswagen. The Auto Union nameplate was discontinued after 1964, but Auto Union's logo -- four interlocking rings to represent its four interlocked companies -- remains the nameplate on present-day Audi vehicles. Father: Karl Horch (blacksmith) Mother: Helene Michel Horch Wife: Anna Schulz Horch (m. Sep-1897, adopted twins in 1928, d. 1946) Wife: Else Kolmar Horch (m. 1948)
University: BS Engineering, Mittweida College (1890)
Teacher: Engineering, University of Braunschweig (1944-48)
Audi Founder & President (1910-20)
August Horch & Co. Founder & President (1899-1909)
Benz & Company Factory Mgr. (1896-99)
Automotive Hall of Fame
German Ancestry
August Horch was a pioneering German entrepreneur who founded not one but two auto companies that bore his name.
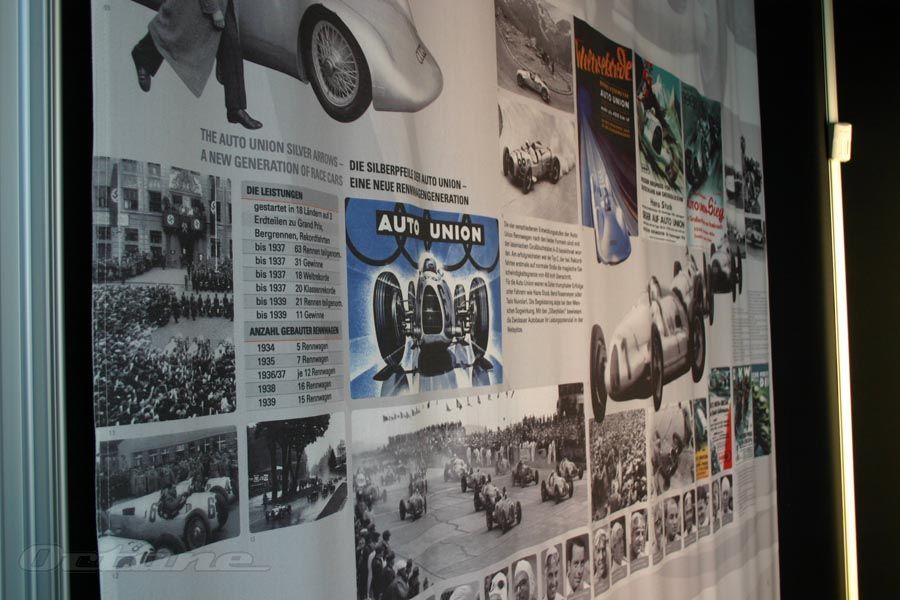
Horch was one of a generation of automotive executives and entrepreneurs who drew both inspiration and practical experience from Daimler and Benz. Horch worked as production manager for Carl Benz for three years starting in 1896. Horch drew on that to found his own business, August Horch & Cie, in November 1899. Within a year he was road testing his company's first automobile. Horch established himself as an engineering innovator from the start. His first car had a friction clutch and shaft-driven rear wheels. He built his first four-cylinder car in 1903 and introduced a six-cylinder model four years later. Horch cars were considered advanced alternatives to the models produced by large brands including Benz and Mercedes. In 1904, economic troubles forced Horch to move the company from Cologne to Zwickau in the eastern German state of Saxony and to convert his business into a joint-stock company, a move he would later regret. Following a dispute in 1909, Horch's shareholders forced him to step down. He later lost the right to use the Horch name on his cars. The setbacks didn't stop Horch for long. He established a new car company in 1910, naming it Audi, the Latin translation of his surname. The first Audis were successful in racing and rallying events but demands of the times -- Horch was forced to supply the military with armored vehicles -- slowed the company's development. After World War I, he led Audi and became involved with government boards regulating the automobile, serving as a representative for the auto industry. Financial difficulties forced Horch to sell Audi to the newly formed Auto Union conglomerate in 1932. That company also had absorbed Horch's former business. But because of his broad contributions to the auto industry, Horch was named an honorary citizen of Zwickau and became an honorary professor at Braunschweig Technical University prior to his death in 1951. He published his autobiography, I Made Cars, in 1937. http://www.autonews.com/files/euroauto/inductees/horch2004.htm Today the Audi name is synonymous with the expression "vorsprung durch technik," which means advantage through technology. But the company has a history going back more than 100 years to the pioneering days of automobile manufacture. In 1899, August Horch established his first company A. Horch & Cie in Cologne. His first car had a 4-5 hp horizontal engine with several innovative design features, and this vehicle was introduced to the public in 1901. The company relocated to Reichenbach in 1902, but the popularity of the Horch cars made it necessary to move again to a larger factory. So in 1904 A. Horch & Cie. Motorwagen - Werke AG was established in Zwickau. In 1909, August Horch entered into a bitter dispute with the supervisory board of the share - issuing corporation that he had created. He left the company and tried to set up Horch Automobil - Werke GmbH, but lost the legal battle to retain the Horch name. So the Audi brand was born - a Latin translation of "horch" (hark in English) -and in 1910 Audiwerke GmbH was established. By 1911, August Horch was entering motorsport events such as the International Austrian Alpine Run. Individual success on the 1911 event led to Audi entries winning the team prize each year from 1912 to 1914. In 1921 Audi became the first German manufacturer to produce a car with left hand drive. Prior to that cars had been right hand drive, a configuration dating back to the age of the horse and carriage, when the coachman sat on the right. Meanwhile the old Horch-werke company in Zwickau had been working on a luxury 8-cylinder car, and in 1926 the 3132cc Horch 303 Berlin became available. In 1927 the DKW motorcycle company also moved into the car market with a vehicle powered by a 2-cylinder engine. Yet another company, Wanderer (established in 1913), had became a significant producer of small cars. In June 1932 the four motor vehicle brands Audi, DKW, Horch and Wanderer joined forces to create Auto Union AG, and adopted the four rings emblem that is today's Audi logo. The new Auto Union company was involved in all segments of the market, from motorcycles to luxury cars. The Auto union racing cars were extremely successful with high performance engines complementing aerodynamic design and lightweight construction. But Auto Union were also involved in the production of special vehicles for military purposes, and following the outbreak of war in 1940 civilian vehicle manufacture ceased. The unfortunate consequence of military involvement was that after the war the Auto Union factory was dismantled, and in 1948 the name Auto Union AG was deleted from the Commercial Register. In 1949 various loans were available to regenerate German industry, and Auto Union GmbH was formed in Ingolstadt. At first production was aimed at motorcycles, to be followed by a small DKW delivery van, and then the first post-war DKW car. Motorcycle production carried on until 1958, at which time the Auto Union company became a fully owned subsidiary of the Stuttgart-based Daimler Group. The company ownership changed again in 1965, and since that time Auto Union (latterly Audi) has been part of the Volkswagen Group. The Audi 100 was introduced in 1968; it became a best seller and ensured the future independence of the Audi brand. The Audi 80 followed in 1972, a car which went on to sell over one million within six years. Then came the Audi Quattro, a four wheel drive high performance sports coupe. This car caused a genuine sensation at the 1980 Geneva Motor Show, and the Audi Quattro with its permanent four wheel drive went on to enjoy world-wide success in motorsport. Through the 1980's, continuing development led to the appearance of quattro (4 wheel drive) versions of the entire model range, the production of an all-alloy V8 engine, and (in 1989) an Audi 100 with a five-cylinder diesel direct injection engine. From 1994 new models of the Audi 80 became known as the A4, whilst the Audi 100 became the A6. For some years Audi had been working on the use of aluminium to produce lighter production cars, and this culminated in the announcement of the Audi A8 at the 1994 Geneva Motor Show. The A8 had an all-aluminium body, a V8 engine, and was aimed squarely at the premium end of the market. Since then the small Audi A2 was launched in 2000; this is the first volume built aluminium car. CJ Clark, 07/03. http://www.germansportscars.com/audi.htm Horch At the end of the 19th century, there were already a number of car manufacturers in Germany. One of them was August Horch & Cie., founded on November 14, 1899 in Cologne. August Horch was one of the pioneer figures of automotive engineering. Before setting up business on his own, he worked for Carl Benz in Mannheim for three years as Head of Automobile Production. In 1904, August Horch relocated his company to Zwickau and transformed it into a share-issuing company. However, in 1909 August Horch withdrew from the company he had founded, and set up a new enterprise under the name of "Audi". Audi The company established by August Horch in Zwickau on July 16, 1909 could not again take its founder's name for reasons of fair trade. Horch found a new name for the company by translating his name, which means "hark!", "listen!", into Latin. So it was that the second company to have been set up by August Horch commenced operations under the name Audi Automobilwerke GmbH, Zwickau, on April 25, 1910. Wanderer In 1885, the two mechanics Johann Baptist Winklhofer and Richard Adolf Jaenicke opened a repair business for bicycles in Chemnitz. Shortly afterwards they began to make bicycles of their own, since demand at that time was very high. These were sold under the brand name Wanderer, and in 1896 the company itself began to trade as Wanderer Fahrradwerke AG. Wanderer built its first motorcycle in 1902. The idea of branching out into automobile production was finally put into practice in 1913. A small two-seater by the name of "Puppchen" heralded in Wanderer's tradition of motor car production that was to last several decades. DKW Originally founded under the name Rasmussen & Ernst 1902 in Chemnitz, the company was moved to Zschopau in the Erzgebirge region in 1907. The company initially manufactured and sold exhaust-steam oil separators for steam-raising plant, mudguards and lighting systems for motor vehicles, vulcanization equipment and centrifuges of all kinds. The company's founder rgen Skafte Rasmussen began to experiment with a steam-driven motor vehicle in 1916, registering DKW as a trademark. In 1919 the company, by now renamed Zschopauer Motorenwerke, switched to the manufacture of small two-stroke engines, which from 1922 on served as a springboard for its success in building motorcycles under the brand name DKW. The first small DKW motor car appeared on the market in 1928. Auto Union AG, Chemnitz On June 29, 1932, Audiwerke, Horchwerke and Zschopauer Motorenwerke - DKW merged on the initiative of the State Bank of Saxony to form Auto Union AG. A purchase and leasing agreement was concluded at the same time with Wanderer, for the takeover of its Automobile Division. The new company's head offices were in Chemnitz. Following the merger, Auto Union AG was the second-largest motor vehicle manufacturer in Germany. The company emblem, with four interlinked rings, symbolized the inseparable unity of the four founder-companies. The brand names Audi, DKW, Horch and Wanderer were retained. Each of the four brands was assigned a specific market segment within the group: DKW assumed responsibility for motorcycles and small cars; Wanderer built midsize cars; Audi manufactured cars in the deluxe midsize class, and Horch produced deluxe top-of-the-range automobiles. Auto Union GmbH, Ingolstadt In 1945, after the end of the Second World War, Auto Union AG was expropriated by the occupying Soviet forces. The company's leading figures consequently moved to Bavaria, where a new company was founded in Ingolstadt in 1949 under the name of Auto Union GmbH, to uphold the motor vehicle tradition of the company with the four-ring emblem. The first vehicles to leave the company's production line after its new start were DKW's successful models with two-stroke engines - motorcycles, cars and delivery vans. A new Auto Union model appeared on the market in 1965, the company's first post-war vehicle with a four-stroke engine. To emphasize this dawning of a new era, a new product name was likewise needed: the traditional name of Audi was resurrected. A short time later, the last DKWs rolled off the production line in Ingolstadt. From then on, the new models with four-stroke engines were produced under the brand name "Audi". A new era had begun in another sense, too: the Volkswagen Group acquired the Ingolstadt-based company in 1965. NSU NSU was founded in 1873 in Riedlingen, on the Danube, by the two Swabian mechanics Christian Schmidt and Heinrich Stoll. Seven years later they moved the company to Neckarsulm. For its first twenty years, the company manufactured knitting machines. Neckarsulmer Strickmaschinenfabrik diversified into bicycles in 1886. From then on, the bicycle was to have a decisive influence on the company's fortunes. Motorcycle production commenced at NSU in 1901, and five years later the first motor car was built there. Automobile production activities were halted again in 1929, to allow the company to concentrate on building two-wheelers. It was almost thirty years later, in 1958, that production of cars recommenced in Neckarsulm. On March 10, 1969, Auto Union GmbH of Ingolstadt merged with NSU Motorenwerke AG, of Neckarsulm. The new company bearing the name Audi NSU Auto Union AG, with its head offices in Neckarsulm, was created retrospectively as of January 1. AUDI AG The last NSU left the production line in March 1977, and from then on the company manufactured exclusively Audi cars. About this time, the company's bosses began to consider streamlining the company's rather cumbersome name of Audi NSU Auto Union AG. With the objective of giving the company and its products the same name, in 1985 Audi NSU Auto Union AG was renamed simply AUDI AG. To coincide with the change of name, the company's registered headquarters were transferred from Neckarsulm to Ingolstadt. Together with the two traditional companies Auto Union GmbH and NSU GmbH, Audi Tradition nurtures and presents the deep and diverse history of Audi. The Audi museum mobile at the Ingolstadt plant is open every day of the week from 9 a.m. to 6 p.m. http://www.worldcarfans.com/104072110429/the-history-of-the-four-rings 





















|
AUDI 4000 4 CYL Parts * AUDI 4000 5 CYL Parts * AUDI 5000 Parts * AUDI 5000 Turbo Parts * AUDI Coupe Parts * AUDI Coupe QT Parts * AUDI 4000 Q Parts * AUDI 80 4 CYL Parts * AUDI 90 5 CYL Parts * AUDI 90 4 CYL Parts * AUDI 90 Q Parts * AUDI S4 Q Turbo Parts * AUDI V8 Q Parts * AUDI 100 V6 Parts * AUDI 100 Q V6 Parts * AUDI 90 V6 Parts * AUDI A4 V6 2.8L-30V Parts * AUDI A4 Quattro V6 30V Parts * AUDI A4 Quattro Turbo Parts * AUDI A6 Quattro Parts * AUDI A8 Quattro Parts * AUDI S4 Q Twin Turbo Parts * AUDI TTParts * AUDI TT Quattro Parts * AUDI S4 Cabrio V8 Parts * AUDI A6 Quattro V8 Parts * AUDI TT Quattro V6 Parts *
AUDI Accessories AUDI Aftermarket Parts AUDI Air Filter AUDI Air Intake Parts AUDI Alternators AUDI Antenna AUDI Axle AUDI Ball Joint AUDI Belts AUDI Body Electrical AUDI Body Mechanical & Trim AUDI Brake Booster AUDI Brake Caliper AUDI Brake Dust Shields AUDI Brake Discs AUDI Brake Hose Brake Pads AUDI Brake Master Cylinder AUDI Brake Pads AUDI Brakes AUDI Catalytic Converter AUDI Clutch AUDI Clutch Disc AUDI Clutch Kit AUDI Clutch Master Cylinder AUDI Clutch Slave Cylinder AUDI Clutch Pressure Plate AUDI Clutch Release Bearing AUDI Coil Springs AUDI Control Arm AUDI Cooling System Auxiliary Fan Assembly AUDI Cooling System Auxiliary Fan Motor AUDI Cooling System Auxiliary Fan Switch AUDI Cooling System Expansion Tank AUDI Cooling System Radiator AUDI Cooling System Radiator Hose AUDI Cooling System Thermostat AUDI Cooling System Thermostat Housing AUDI Cooling System Thermostat Housing Cover AUDI Cooling System Water Pump AUDI CV Boot AUDI CV Joint AUDI Diesel Injection AUDI Distributor cap AUDI Distributor Rotor AUDI Drive belts AUDI Driveshaft and Axle Assembly parts AUDI Engine mounts AUDI Engine Parts AUDI Exhaust AUDI Fan Blade AUDI Fan Clutch AUDI Fog Light AUDI Fuel Filter AUDI Fuel Injectors AUDI Fuel Injection parts AUDI Fuel Pump AUDI Grille AUDI Head Gasket AUDI Headlights AUDI Heater Core AUDI Ignition Coil AUDI Master Cylinder AUDI Motor Mount AUDI Mufflers AUDI OEM Parts AUDI Oil Filter AUDI Oxygen Sensor AUDI Power Steering parts AUDI Power Steering Pump AUDI Pressure Plate AUDI Radiator AUDI Radiator Fan AUDI Radiator Hose AUDI Relay AUDI Repair Manuals AUDI Rotors AUDI Shock Absorber AUDI Shocks AUDI Spark Plugs AUDI Spark Plug Wires AUDI Spoiler AUDI Starter AUDI Steering Rack AUDI Strut Mount AUDI Struts AUDI Tail Light Guards AUDI Tail Lights AUDI Thermostat AUDI Tie Rods AUDI Timing Chain AUDI Transmission Mount AUDI Transmission parts AUDI tune up parts AUDI Turn Signal AUDI Valve Cover Gasket AUDI Water Pump AUDI Wheel Bearing AUDI Window Motor AUDI Wiper Blade VolksWagen  jetta /passat / golf / GTI / beetle
jetta /passat / golf / GTI / beetle
porsche audi 
WORLD REKNOWN SPECIALISTS bmw 
mercedes FORD 
GM chrysler datsun jaguar 
 austinHEALY austinHEALY
|
Audi R8 5.2 FSI quattro benefits from the company's cutting-edge racing technologies.
Audi, as the first global premium auto brand to make cars in China, now has more than 20 years of experience in the nation, a history that is now an important part of its century-old lineage.
Audi was founded by August Horch in Germany in 1909. When he started a new company with his own name, he was soon a victim of trademark infringement by his former partners - and was in fact banned by the courts from using his own family name on any future designs.
But he soon found a new name with the help of his partner's son.
The son was studying Latin during a meeting and suddenly shouted "horch," which means "hark" or "listen" in German - or "audi" in Latin.
August Horch thought it was a sensational idea to connect Horch with Audi. He immediately adopted the company name in 1910.
In 1928, the Audi brand was bought by J S Rasmussen, who acquired a majority shareholding in Audiwerke AG. Four years later Audi merged with four other German car manufacturers from the Saxony area.
Audi, DKW, Horch and Wanderer became Auto Union AG in 1932 with the new logo consisting of four rings to symbolize the joining of these four historic names in German motor manufacturing.
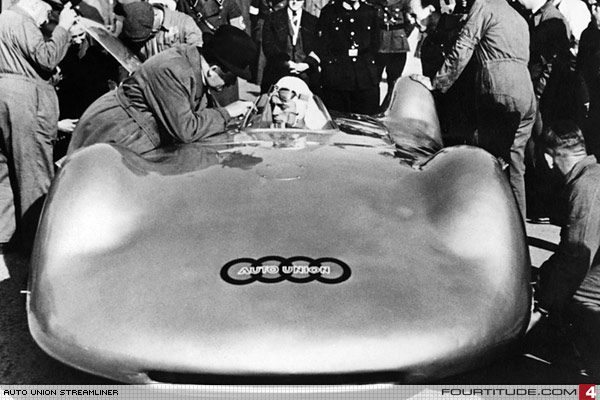
The larger company was able to supply passenger vehicles across the market, from motorcycles to luxury saloons, and become the second-largest car company in Germany. In the 1930s, its car production took a quarter of the car market in Germany and its annual capacity surpassed 67,000 units.
However, the Audi name was severely damaged in World War II. In the late 1930s Auto Union AG started to produce military vehicles for war demands and stopped the civilian vehicle production.
After the war, the Soviets dismantled Auto Union's factories in 1945 and in 1948 the company was removed from the commercial register.
However, Audi's people never gave up rebuilding the brand. They approached the Bavarian government, which granted a loan, so the Audi name survived and began to carve out a second incarnation.
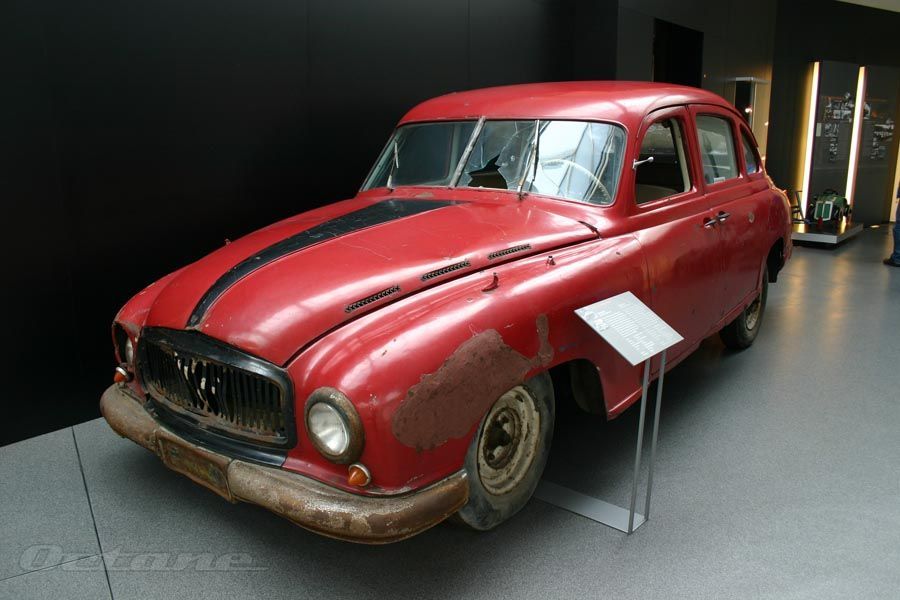
In 1949, Auto Union GmbH Audi was formed in Ingolstadt. In 1955 the new company produced the most popular car of the 1950s on German car market, the P94 sedan.
The company was bought by Volkswagenwerk AG in December 1964.
In 1968, the Audi 100 was launched. This quickly became a top seller with the sales of 800,000 units amongst upper mid-sized cars, and became the benchmark for a new Audi range. In 1972 the Audi 80 was launched.
The Audi 80 became a huge success and over 1 million were built within six years. Its four-cylinder engine was adopted by the Volkswagen Group.
In 1974, the Audi 50 was launched into the small car market. Six months later, production synergies were developed with the Volkswagen brand and the VW Polo was launched, based on the Audi 50.
In 1980, the now-famous Audi Quattro was launched, the first performance car with four-wheel drive.
The company officially became known as Audi AG in 1985, which is testimony to survival and success of the Audi brand.
Developing in China
During Audi's golden time of development it also pioneered the premium sedan market in China in 1986.
In 1986, Audi AG made its first official contact with China and together with First Automotive Works (FAW) began a joint feasibility study. That year, a total of 499 Audi cars were assembled in Changchun.
In 1990, FAW installed assembly lines for Audi cars with a daily capacity of 50 units. In 1993, Audi joined the joint venture of FAW-VW. In 1995, FAW-VW began to prepare for the production of the Audi 200 V6 - a model developed solely for China. In the following year, the Audi 200 V6 came off the production line.
In 1996, Audi established an after-sales service division in Beijing. An expert team of professionals was assembled and four years later the first Audi standard dealer's showroom opened in Beijing.
Buoyed by a new sales record in China, the Audi A6, A8, new Audi A4 and the Audi TT sports car were launched in China from 1999 to 2001. Audi's sales in China soon increased to 27,890 units by 2001.
In 2002, an updated Audi A6 with 23 improved components, as well as xenon headlights, parking heaters and electric seats, helped Audi lead in the premium car market in China. One year later, the new Audi A8 was also launched in China.
In May 2004, the Audi A8L 6.0 quattro 4WD, the high-class flagship product of Audi, came off the production line. With the most advanced technology and best performance, it became one of the leaders in the Chinese premium car market.
In August 2004, the China-made Audi A6 2.5 TDI diesel was officially launched. That year Audi's sales increased by 0.8 percent to reach 64,018 units, including 46,177 units of the China-made Audi A6 and 15,841 units of the China-made Audi A4.
In April 2005, the new China-made Audi A6L was launched. In October, the introduction of the new Audi A4 further consolidated and completed the Audi product line in China.
In July 2006, the Audi Q7, combining many Audi proprietary advanced technologies and world-class SUV designs, was officially launched in China.
In 2006, the FAW-VW Audi Sales Division was established in Changchun. Its dealer network in China now spans 89 cities and with 144 dealers.
While providing advanced products and services to Chinese customers, Audi also joins in China's premier sports and cultural activities, including the "Driving Dreams" program, the "Audi Premium Club" and the Beijing International Music Festival.
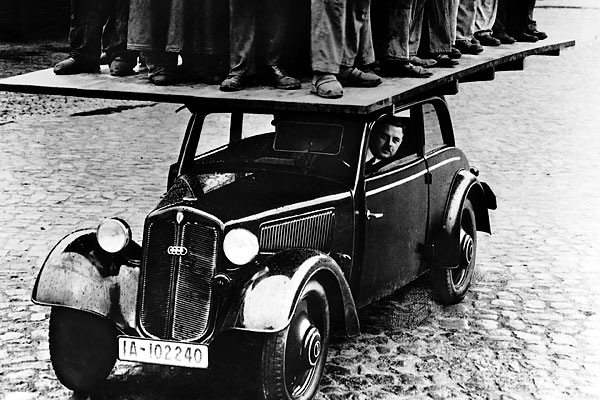
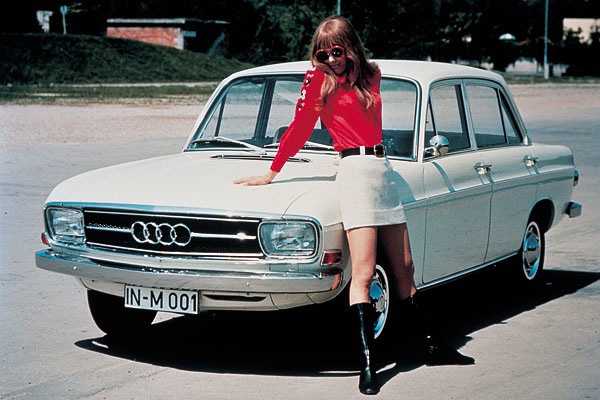
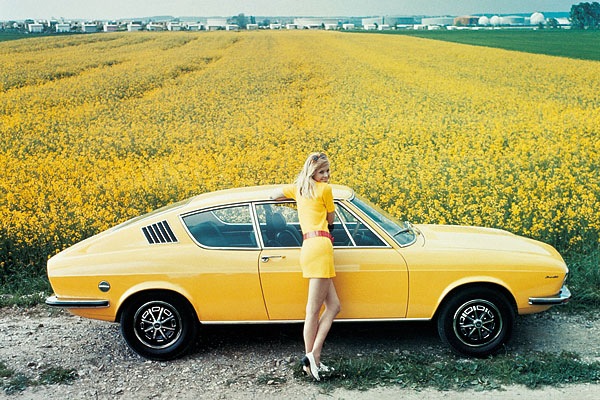
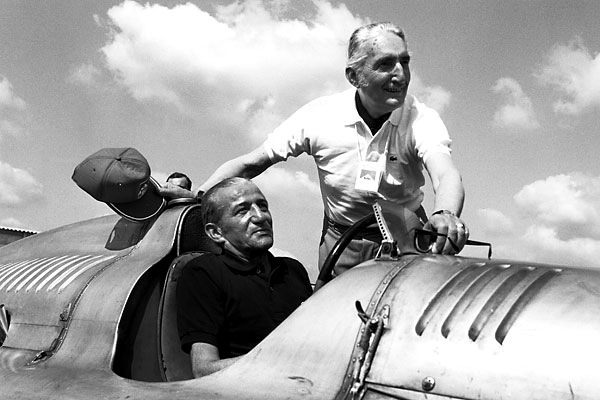
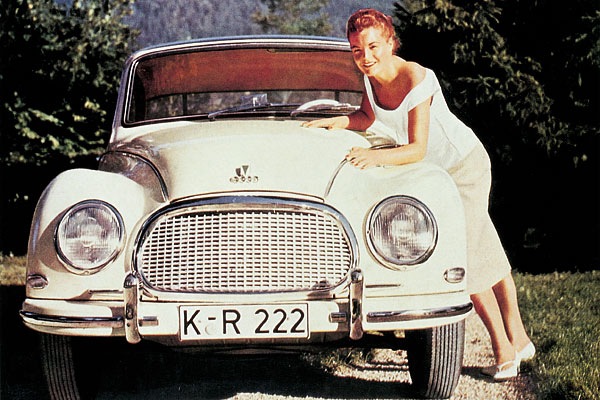
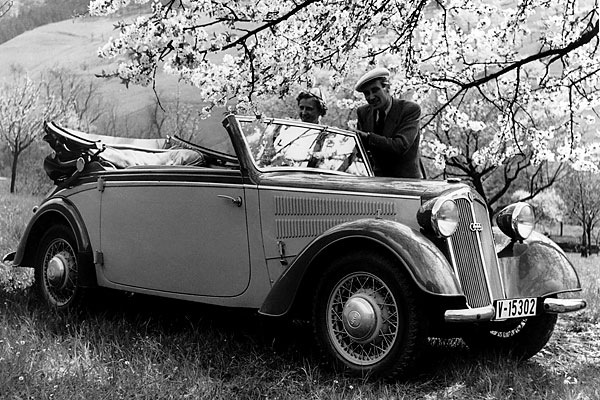
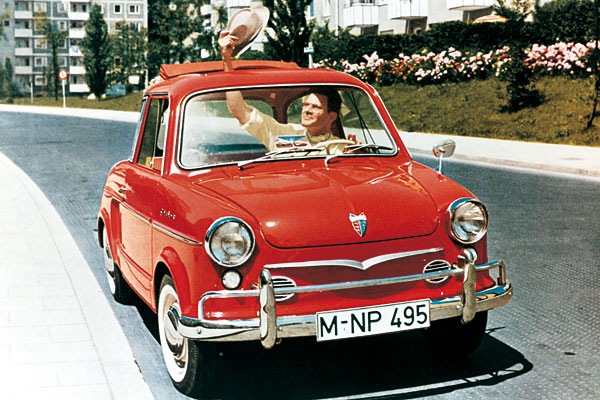
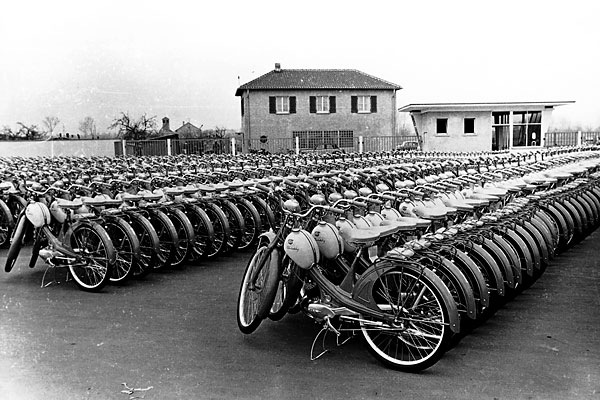
























BENTLEY w/ AUDI motor
